Lectins are proteins or glycoproteins which possess the ability to bind specifically sugars. They have no enzyme activity and are not antibodies. Lectins are ubiquitous in nature, being found in all kinds of organisms (virus, microorganisms, plants, invertebrates and vertebrates). Lectins are usually oligomeric proteins and have many binding sites. The binding constant of the specific free sugar is generally many orders of magnitude lower than the binding constant of a glycoconjugate (glycolipid, glycoprotein...) containing this sugar. Lectins agglutinate cells, some lectins are even blood type specific, but they are also able to recognize cells surface glycans allowing to distinguish between different cells species and states. Furthermore some lectins stimulate lymphocyte and induce mitosis.
The lectins have been used for :
- Studies of glycobiological interactions with glycans or glycans mimics
- Detection, isolation, and structural studies of glycoproteins
- Study the dynamics of the cell surface glycoconjugates
- Cell identification and to separate subpopulation of cells and subcellular organelles
- Study endocytosis, neoplastic transformation
- Mitogenic stimulation of lymphocytes
- Design diagnostics assays
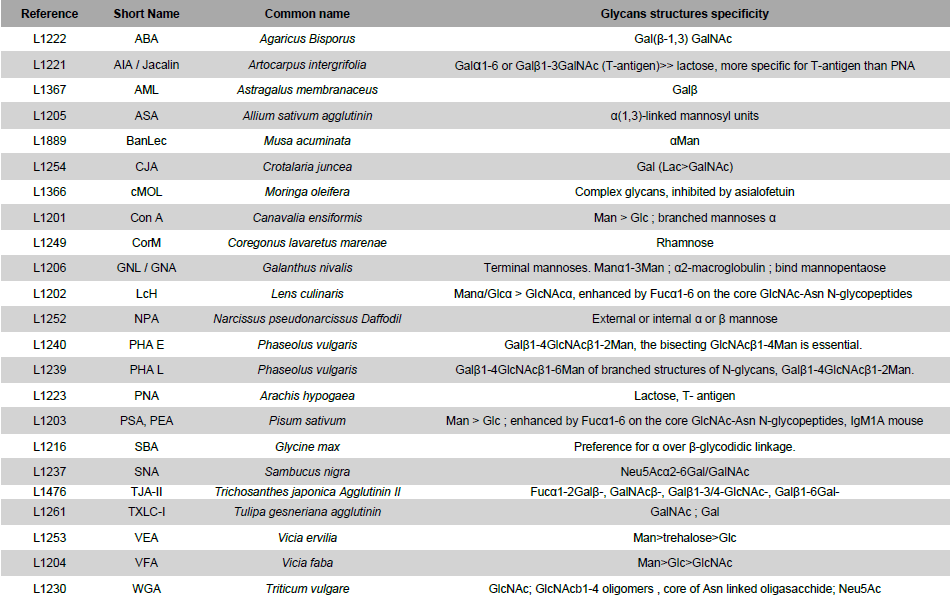
References of naturals lectins currently available:
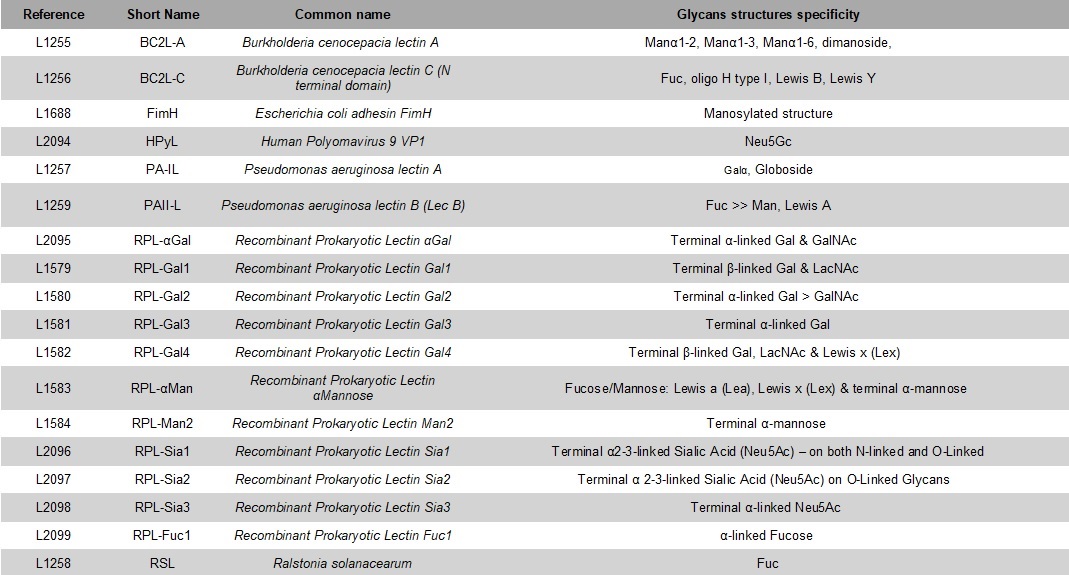
References of recombinants lectins currently available: